
This week, we briefed our clients on ConsentFix, which allows a threat actor to access a victim's Microsoft account without a password or MFA prompt.
KEY TAKEAWAYS
-
New ClickFix-style account hijacking technique called “ConsentFix”. Learn how to protect your organization.
-
Critical and high-severity vulnerabilities in React, Fortinet, SAP, and Microsoft, plus updates to CISA KEV, patch now!
New ClickFix Variant "ConsentFix"
As reported in the last Threat Intel Report, ClickFix attacks have become the most common social engineering attack method in 2025. On December 11, 2025, researchers at Push Security detailed a highly sophisticated variant of the ClickFix attack they dubbed "ConsentFix". What makes this variation unique and especially dangerous, is unlike other variants where the end result is the victim downloading or running malicious code, ConsentFix is instead used to phish the victim's Microsoft OAuth token, which the threat actor then uses to log into Azure CLI. Since no code is executed on the victim's machine, this attack leaves a much smaller footprint, making it difficult to detect.
How ConsentFix Works
Users first visit the malicious or compromised site via a Google search. According to Push Security's research, the majority of sites serving this attack are legitimate, compromised websites. The victim is first presented with a fake Cloudflare prompt, asking for the victim to enter their email address. This textbox filters for valid business email addresses and will not continue if a personal email address is entered.
 Fig. 1: Fake Cloudflare Turnstile Page | Source: Push Security
Fig. 1: Fake Cloudflare Turnstile Page | Source: Push Security
Once a "valid" email address is entered, the victim is taken to the second stage. Here they are prompted to sign in to their Microsoft account to "verify their identity":
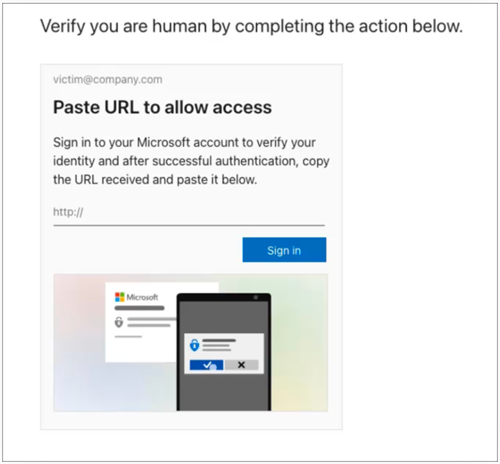
Fig. 2: Second phase of ConsentFix attack Source: Push Security
When the victim clicks the "Sign In" button, a new tab is opened in the browser which leads to a legitimate Microsoft sign-in page. If the victim is already signed into their Microsoft account, they simply need to click the user account from the dropdown. Otherwise, the victim authenticates to their Microsoft account. Once this action is completed, the victim is redirected in the browser to localhost, where a URL is generated containing a code associated with the victim's Microsoft account. The victim then pastes this URL into the prompt and clicks "Next".
As soon as this step is completed, the threat actor is given access to the victim's Microsoft account via Azure CLI. This gives the threat actor control over the victim's Microsoft account without needing the victim's password or needing to pass an MFA check.
How to Protect Your Organization
- As with all social engineering attacks, user awareness training is paramount. Users must be made aware of ClickFix-style attacks, so they are less likely to fall for them.
- Follow the principle of least privilege and restrict access to Azure Management Apps (including Azure CLI) for non-privileged users via Conditional Access Policies in Azure (Entra) ID.
- Hunt for suspicious sign-ins to Microsoft Azure CLI using the Application ID: 04b07795-8ddb-461a-bbee-02f9e1bf7b46
- Look for non-interactive sign-ins shortly after the suspicious Azure CLI interactive sign-ins.
- Look for IP addresses or geolocations that do not match the user's baseline.
- Enable AADGraphActivityLogs to monitor legacy scopes such as AD enumeration commands.
Resources:
-
https://azvise.com/2022/08/18/restrict-access-to-azure-management-apps-azure-ad/
-
https://github.com/MicrosoftDocs/entra-docs/blob/main/docs/identity/conditional-access/concept-conditional-access-cloud-apps.md#windows-azure-service-management-api
-
https://www.bleepingcomputer.com/news/security/new-consentfix-attack-hijacks-microsoft-accounts-via-azure-cli/
Vulnerability Roundup
Maximum-Severity Flaw in React Server Components (React2Shell)
On December 3rd, a maximum-severity vulnerability was disclosed for React Server Components. The vulnerability, tracked as CVE-2025-55182 and referred to as "React2Shell", is an unauthenticated remote code execution vulnerability. It affects versions 19.0, 19.1.0, 19.1.1, and 19.2.0 of the react-server-dom-webpack, react-server-dom-parcel, and react-server-dom-turbopack packages. These packages are used as dependencies by other frameworks, including Next.js, React Router, Waku, Parcel, Vite, and RedwoodSDK. This vulnerability is under widespread exploitation, and administrators are urged to upgrade as soon as possible. For a detailed writeup on how this vulnerability works, and more importantly, how to detect and mitigate the vulnerability, please see our Responding to React2Shell writeup by Andy Oesterheld, Brandon Schwartz, and Jon Ingram.
- https://packetwatch.com/resources/blog/responding-to-react2shell
- https://react.dev/blog/2025/12/03/critical-security-vulnerability-in-react-server-components
- https://www.rapid7.com/blog/post/etr-react2shell-cve-2025-55182-critical-unauthenticated-rce-affecting-react-server-components/
- https://www.wiz.io/blog/critical-vulnerability-in-react-cve-2025-55182
- https://aws.amazon.com/blogs/security/china-nexus-cyber-threat-groups-rapidly-exploit-react2shell-vulnerability-cve-2025-55182/
Additional Vulnerabilities in React Server Components (RSC)
Due to the increased scrutiny of RSC because of React2Shell, 3 additional vulnerabilities were quickly discovered.
- CVE-2025-55184 and CVE-2025-67779 - A pre-authentication denial of service vulnerability due to unsafe deserialization of payloads from HTTP requests. Successful exploitation can trigger an infinite loop that hangs the server process.
- CVE-2025-55183 - An information leak vulnerability, where a specially crafted HTTP request sent to a vulnerable Server Function can return the source code of any other Server Function. There is a special condition for this vulnerability: It requires the existence of a Server Function that explicitly or implicitly exposes an argument that has been converted into a string format.
These vulnerabilities affect the following packages: react-server-dom-webpack, react-server-dom-parcel, react-server-dom-turbopack. Administrators are urged to update these packages to versions 19.0.3, 19.1.4, or 19.2.3 as soon as possible.
- https://react.dev/blog/2025/12/11/denial-of-service-and-source-code-exposure-in-react-server-components
- https://thehackernews.com/2025/12/new-react-rsc-vulnerabilities-enable.html
Fortinet FortiCloud SSO Login Auth Bypass
Last week, Fortinet released security fixes for two vulnerabilities that can allow attackers to bypass FortiCloud SSO authentication. CVE-2025-59718 affects FortiOS, FortiProxy, and FortiSwitchManager. CVE-2025-59719 affects FortiWeb. It should be noted that the FortiCloud SSO feature is not enabled by default, but is enabled if administrators have registered the device to FortiCare via the device's GUI. Administrators are urged to disable the FortiCloud login feature until the device is upgraded to a non-vulnerable version.
- https://www.fortiguard.com/psirt/FG-IR-25-647
- https://www.bleepingcomputer.com/news/security/fortinet-warns-of-critical-forticloud-sso-login-auth-bypass-flaws/
Multiple Critical Vulnerabilities in SAP Products
In their December security updates, SAP released fixes for 14 new vulnerabilities, 3 of which are rated critical.
- CVE-2025-42880 - A code injection vulnerability in SAP Solution Manager ST 720. An authenticated attacker can insert malicious code when calling a remote-enabled function module, leading to full control of the system.
- CVE-2025-55754 - Addresses multiple Apache Tomcat vulnerabilities affecting SAP Commerce Cloud components in versions HY_COM 2205, COM_CLOUD 2211, and COM_CLOUD 2211-JDK21. Successful exploitation can allow the attacker to trick an administrator into running an attacker-controlled command.
- CVE-2025-42928 - A deserialization vulnerability affecting SAP jConnect (a JDBC driver used to connect Java applications to SAP ASE and SAP SQL Anywhere databases). Successful exploitation allows for a high-privileged user to achieve remote code execution.
Administrators are urged to apply patches as soon as possible.
- https://www.bleepingcomputer.com/news/security/sap-fixes-three-critical-vulnerabilities-across-multiple-products/
- https://www.cve.org/CVERecord?id=CVE-2025-42880
- https://www.cve.org/CVERecord?id=CVE-2025-55754
- https://www.cve.org/CVERecord?id=CVE-2025-42928
Microsoft PowerShell Remote Code Execution Vulnerability
As part of the December Patch Tuesday release, Microsoft addressed CVE-2025-54100, a remote code execution vulnerability in PowerShell. The "fix" is a warning that will be displayed when using the "Invoke-WebRequest" cmdlet, which warns the user that scripts contained in web pages downloaded using the cmdlet could execute on your system. By pressing the default with "Enter" or selecting "No", the operation is cancelled, and PowerShell will suggest running the command with the "-UseBasicParsing" parameter instead. Admins should be aware of this change as it may affect automation scripts and update them accordingly. It should also be noted that when 'curl' is run in PowerShell, it aliases the "Invoke-WebRequest" cmdlet, so these warnings will also affect scripts invoking "curl" commands.
- https://msrc.microsoft.com/update-guide/vulnerability/CVE-2025-54100
- https://www.bleepingcomputer.com/news/security/microsoft-windows-powershell-now-warns-when-running-invoke-webrequest-scripts/
CISA KEV Additions
The following vulnerabilities were added to CISA's Known Exploited Vulnerabilities Catalog in the last 2 weeks:
- CVE-2025-14174 - Google Chromium Out of Bounds Memory Access Vulnerability
- CVE-2018-4063 - Sierra Wireless AirLink ALEOS Unrestricted Upload of file with Dangerous Type Vulnerability
- CVE-2025-58360 - OSGeo GeoServer Improper Restriction of XML External Entity Reference Vulnerability
- CVE-2025-62221 - Microsoft Windows Use After Free Vulnerability
- CVE-2025-6218 - RARLAB WinRAR Path Traversal Vulnerability
- CVE-2025-66644 - Array Networks ArrayOS AG OS Command Injection Vulnerability
- CVE-2022-37055 - D-Link Routers buffer Overflow Vulnerability
- CVE-2025-55182 - Meta React Server Components Remote Code Execution Vulnerability
This report is provided FREE to the cybersecurity community.
Visit our Cyber Threat Intelligence Blog for additional reports.
Subscribe to be notified of future Reports:
NOTE
We have enhanced our report with data from SOCRadar. You may need to register to view their threat intelligence content.
DISCLAIMER
Kindly be advised that the information contained in this article is presented with no final evaluation and should be considered raw data. The sole purpose of this information is to provide situational awareness based on the currently available knowledge. We recommend exercising caution and conducting further research as necessary before making any decisions based on this information.

 The PacketWatch Intelligence Team
The PacketWatch Intelligence Team