5 min read
Cyber Threat Intelligence Briefing - October 23, 2023
 The PacketWatch Intelligence Team
:
October 23, 2023
The PacketWatch Intelligence Team
:
October 23, 2023

Welcome back to another week of Cyber Threat Intelligence (CTI). This week's report highlights two critical zero-days from Cisco and critical vulnerabilities in Citrix NetScaler.
Two Critical 0-Days Actively Exploited in Cisco IOS XE Web UI
Last week, Cisco published a security advisory highlighting a critical (CVSS 10.0) zero-day vulnerability in the Cisco IOS XE software.
Tracked as CVE-2023-20198, successful exploitation of this vulnerability allows for a remote unauthenticated attacker to create an account on the system with 'level 15 access'. This permission set allows the user to enter 'Privileged Exec' mode and provides complete control over the device.
Devices in the wild that have been successfully compromised were found to have a malicious Lua (programming language) implant installed that allows for additional access to the system.
It was initially believed that successful installation of this implant was related to a previous Cisco vulnerability, CVE-2023-1435; however, it was later disclosed that a second 0-day, CVE-2023-20273 was being leveraged to install the implant.
Heading into the weekend, internet scanners showed approximately 60,000 devices had been successfully compromised and showed evidence of the malicious implant.
On Sunday, October 22, that number dropped substantially, down to less than 1,000.
Security researchers are unsure as to why this number dropped so significantly, but one of the leading theories is the threat actor updated the implant code and configuration so that it is not as simple to detect remotely.
Affected Products
This vulnerability affects Cisco IOS XE Software if the Web UI feature is enabled, including enterprise switches, access points, wireless controllers, and routers. This feature is enabled via the ‘ip http server’ or ‘ip http secure-server’ commands.
Per the Cisco advisory, administrators can determine whether the HTTP server is enabled on a system by running the following command:
show running-config | include ip http server|secure|active

Fig. 1: Router command per Cisco advisory
Note: Per the advisory, the presence of either command or both commands in the system configuration indicates the Web UI feature is enabled.
Additionally:
- If the ip http server command is present and the configuration also contains ip http active-session-modules none, the vulnerability is not exploitable over HTTP.
- If the ip http secure-server command is present and the configuration also contains ip http secure-active-session-modules none, the vulnerability is not exploitable over HTTPS.
Indicators of Compromise
To determine if a vulnerable system may have already been compromised, administrators can perform the following checks:
Review system logs to check for any log messages where user could be cisco_tac_admin, cisco_support, or “any configured, local user that is unknown to the network administrator”:
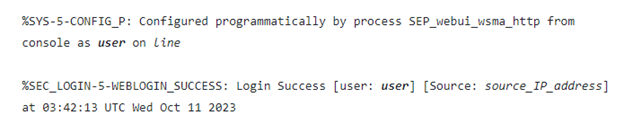 Fig. 2: Cisco system log example
Fig. 2: Cisco system log example
- The %SYS-5-CONFIG_P log message will be present each time a user has accessed the web UI. Check for new or unknown usernames.
- Although the advisory does not go into much detail regarding post-compromise activity, it does include a check to see if an “implant” was installed by an unauthorized user:
 Fig. 3: Cisco system log for file "implant" install
Fig. 3: Cisco system log for file "implant" install
- Additionally, administrators can send a curl request to a potentially affected host to check for the presence of an implant. If the following request returns a hexadecimal string, then the implant is present:
 Fig. 4: Curl request to check for implant (per Cisco)
Fig. 4: Curl request to check for implant (per Cisco)
- Per the advisory, the following Snort rules can also detect attempted exploitation:
- 3:50118:2 - can alert for initial implant injection
- 3:62527:1 - can alert for implant interaction
- 3:62528:1 - can alert for implant interaction
- 3:62529:1 - can alert for implant interaction
- 3:62541 - Covers exploit attempts for initial access (CVE-2023-20198)
- 3:62542 - Covers exploit attempts for initial access (CVE-2023-20198)
- Known external IPs attempting remote exploitation:
- 5.149.249[.]74
- 154.53.56[.]231
- 154.53.63[.]93
- Known usernames created after exploitation:
- cisco_tac_admin
- cisco_support
- cisco_sys_manager
Remediation
As of October 22, Cisco has begun rolling out official fixes for affected product versions. Additional details and the full patch release schedule can be found here.
Until all affected devices can be fully patched and remediated, system administrators are strongly encouraged to identify all Cisco devices that have the HTTP Server feature enabled and disable it. If disabling the HTTP Server is not feasible, then strict access control lists can also mitigate exploitation. Only allow trusted hosts and networks to connect to the device. All identified devices should be thoroughly checked for evidence of the malicious implant and for unauthorized accounts.
Additional Resources
- https://blog.talosintelligence.com/active-exploitation-of-cisco-ios-xe-software/
- https://sec.cloudapps.cisco.com/security/center/content/CiscoSecurityAdvisory/cisco-sa-iosxe-webui-privesc-j22SaA4z
- https://www.cisco.com/c/en/us/support/docs/ios-nx-os-software/ios-xe-dublin-17121/221128-software-fix-availability-for-cisco-ios.html
- https://nvd.nist.gov/vuln/detail/CVE-2023-20198
- https://www.bleepingcomputer.com/news/security/cisco-discloses-new-ios-xe-zero-day-exploited-to-deploy-malware-implant/
- https://www.bleepingcomputer.com/news/security/number-of-hacked-cisco-ios-xe-devices-plummets-from-50k-to-hundreds/
Critical Vulnerability in Citrix NetScaler ADC/Gateway Appliances
On October 10, Citrix released a security bulletin highlighting two vulnerabilities in the NetScaler ADC and NetScaler Gateway platforms.
The first, CVE-2023-4966, carries a critical CVSS rating of 9.4, and is an "unauthenticated buffer-related vulnerability" that can lead to "sensitive information disclosure".
While the original bulletin from Citrix did not disclose what information could be leaked via exploitation, security firm Mandiant has since published documentation stating successful exploitation allows the threat actor to "hijack existing authenticated sessions, bypassing multifactor authentication (MFA) or other authentication requirements". These sessions may also persist even after the patch has been deployed.
The second vulnerability, CVE-2023-4967, carries a high-severity CVSS rating of 8.2, and is a denial of service (DoS) vulnerability. It should be noted that the device must be configured as a Gateway (VPN virtual server, ICA Proxy, CVPN, RDP Proxy) or an AAA virtual server in order to be vulnerable.
Affected Products
The bulletin applies to customer-managed NetScaler ADC and NetScaler Gateway products:
- NetScaler ADC and NetScaler Gateway 14.1 before 14.1-8.50
- NetScaler ADC and NetScaler Gateway 13.1 before 13.1-49.15
- NetScaler ADC and NetScaler Gateway 13.0 before 13.0-92.19
- NetScaler ADC 13.1-FIPS before 13.1-37.164
- NetScaler ADC 12.1-FIPS before 12.1-55.300
- NetScaler ADC 12.1-NDcPP before 12.1-55.300
Note: NetScaler ADC and NetScaler Gateway version 12.1 are now End-of-Life (EOL) and are vulnerable.
Remediation
Administrators are strongly encouraged to patch vulnerable devices as soon as possible. A full list of current firmware versions can be found here. In addition to patching, Mandiant has provided additional steps to ensure persistent access to a compromised device has been removed:
- Terminate all active and persistent sessions (per appliance)
- Connect to the NetScaler appliance using the CLI
- Terminate all active sessions with the following command:
- kill aaa session -all
- Clear persistent sessions across NetScaler load balancers run the following command where <vServer> is the name of the virtual server/appliance):
- clear lb persistentSessions <vServer>
- Clear existing ICA sessions with the following command:
- kill icaconnection -all
- Rotate credentials for identities that were provisioned for accessing resources via a vulnerable NetScaler ADC or Gateway appliance.
- If web shells or backdoors are identified on the NetScaler appliances, it is recommended to rebuild the appliance using a clean-source image, including the latest firmware.
- Reduce the external attack exposure and attack surface of the NetScaler appliances by restricting ingress access to only trusted or predefined source IP address ranges.
Additional Resources
- https://services.google.com/fh/files/misc/citrix-netscaler-adc-gateway-cve-2023-4966-remediation.pdf
- https://support.citrix.com/article/CTX579459/netscaler-adc-and-netscaler-gateway-security-bulletin-for-cve20234966-and-cve20234967
- https://arstechnica.com/security/2023/10/the-latest-high-severity-citrix-vulnerability-under-attack-isnt-easy-to-fix
PacketWatch publishes this report and other cybersecurity threat intel to the security community for free via our blog. If you want personalized threat intel, contact us today to learn about our enterprise threat intelligence services.
Disclaimer
Kindly be advised that the information contained in this article is presented with no final evaluation and should be considered raw data. The sole purpose of this information is to provide situational awareness based on the currently available knowledge. We recommend exercising caution and conducting further research as necessary before making any decisions based on this information.
